
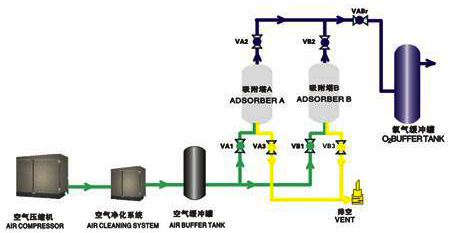
Principle:
After being compressed by an air compressor, the air enters the air storage tank through dust removal, oil removal, and drying. It then passes through the air inlet valve and left inlet valve before entering the left adsorption tower. The tower pressure increases, and nitrogen molecules in the compressed air are adsorbed by zeolite molecular sieves. Unadsorbed oxygen passes through the adsorption bed and enters the oxygen storage tank through the left gas production valve and oxygen production valve. This process is called left adsorption and lasts for several tens of seconds. After the left adsorption process is completed, the left adsorption tower and the right adsorption tower are connected through a pressure equalization valve to achieve pressure equilibrium between the two towers. This process is called pressure equalization and lasts for 3-5 seconds. After the pressure equalization is completed, the compressed air enters the right adsorption tower through the air inlet valve and the right inlet valve. The nitrogen molecules in the compressed air are adsorbed by zeolite molecular sieves, and the enriched oxygen enters the oxygen storage tank through the right production valve and the oxygen production valve. This process is called right adsorption and lasts for several tens of seconds.
At the same time, the nitrogen adsorbed by the zeolite molecular sieve in the left adsorption tower is released back into the atmosphere through the left exhaust valve, and this process is called desorption. On the contrary, when the left tower adsorbs, the right tower also desorbs simultaneously. In order to completely discharge the nitrogen released from the depressurization of the molecular sieve into the atmosphere, oxygen is blown out of the desorption tower through a normally open blowback valve to remove the nitrogen inside the tower. This process is called blowback, which occurs simultaneously with desorption. After the right suction is completed, it enters the pressure equalization process and then switches to the left suction process, continuing to produce high-purity product oxygen continuously.
